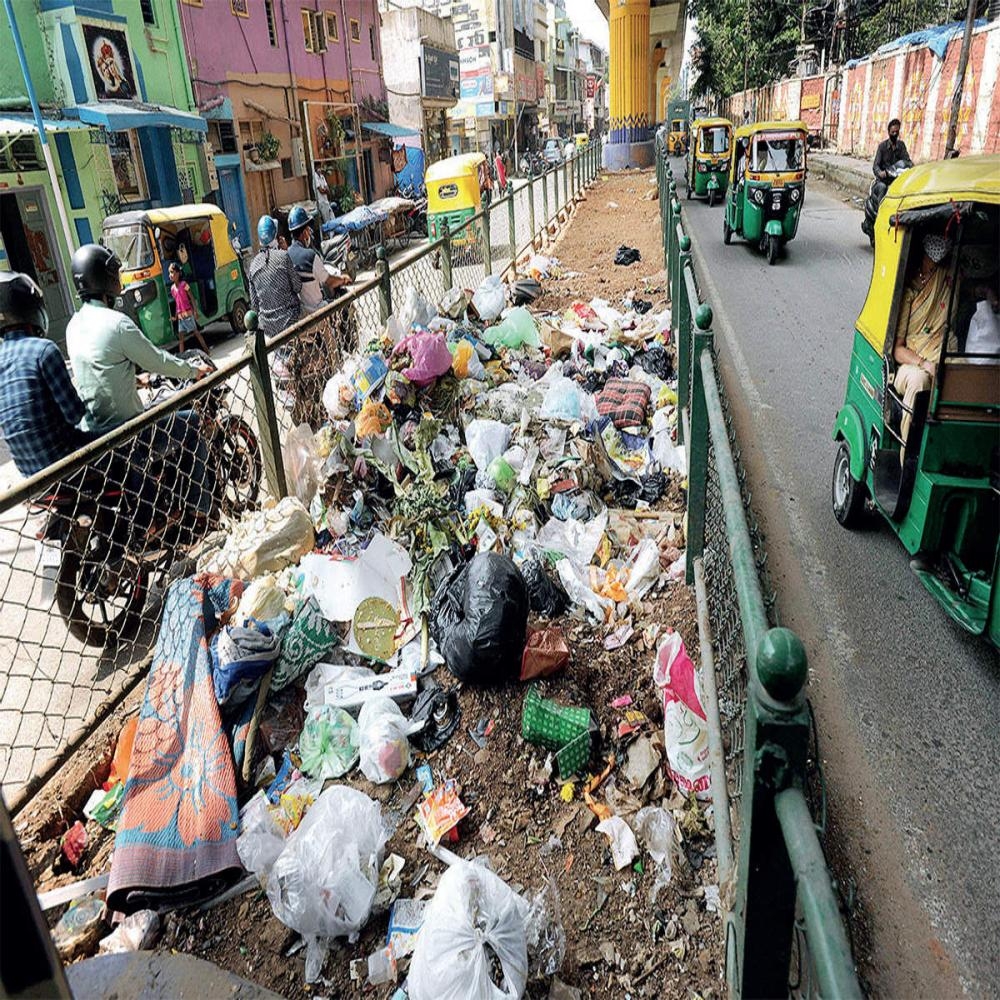
Hazardous waste management is a critical component of environmental protection and public health. Hazardous waste refers to materials that pose significant risks to human health and the environment, including industrial chemicals, medical waste, and certain household items like batteries, pesticides, and paints. Improper disposal of these materials can lead to severe consequences, such as contamination of soil, water, and air, which can cause long-term damage to ecosystems and human health. For example, chemicals seeping into groundwater can render drinking water unsafe, while toxic emissions from improper incineration can contribute to air pollution.
To mitigate these risks, hazardous waste must be handled with care and disposed of in specialized facilities designed to manage its unique properties safely. This is where regulations play a crucial role. Many countries have established stringent laws to oversee the handling, transportation, and disposal of hazardous waste. In the United States, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) provides a legal framework to ensure hazardous waste is managed from its generation to its final disposal. Compliance with these regulations is not just about avoiding legal penalties; it also ensures that businesses and institutions contribute to a safer environment and protect their reputations.
Technological advancements have also made hazardous waste management more efficient and effective. Innovations like automated waste tracking systems, advanced treatment methods, and waste-to-energy technologies have improved the way hazardous waste is handled, reducing environmental impact and creating opportunities for resource recovery. Waste-to-energy technologies, for instance, allow certain types of hazardous waste to be converted into energy, reducing the need for landfills and lowering the overall environmental footprint.
Both individuals and organizations play vital roles in hazardous waste management. For individuals, this might mean properly disposing of household hazardous waste at designated collection facilities or participating in community hazardous waste disposal events. Organizations, on the other hand, must adopt best practices to minimize the generation of hazardous waste, such as implementing cleaner production methods, recycling hazardous materials, or using safer alternatives to hazardous substances. By taking these steps, we can all contribute to reducing the risks associated with hazardous waste and ensure a cleaner, safer environment for future generations.
In conclusion, hazardous waste management is a complex but essential responsibility that safeguards public health and the environment. By following regulations, leveraging technological advancements, and taking proactive measures, both individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the risks posed by hazardous waste, making our world a safer place for all.